Key Points
- Salvia divinorum produces intense hallucinogenic effects through salvinorin A, which acts on different brain receptors than classic psychedelics.
- Common effects include vivid hallucinations, severe time distortion, dissociation, loss of coordination, and unpredictable emotional reactions.
- Salvia is dangerous due to acute risks like accidents during intoxication and potential psychological dangers, including panic and lasting anxiety.
- Effects typically last 15 to 30 minutes but can trigger prolonged psychological aftereffects in some individuals.
- Research on long-term effects is limited, but some users report persistent anxiety, depression, and cognitive disturbances.
What You Need to Know About Salvia:
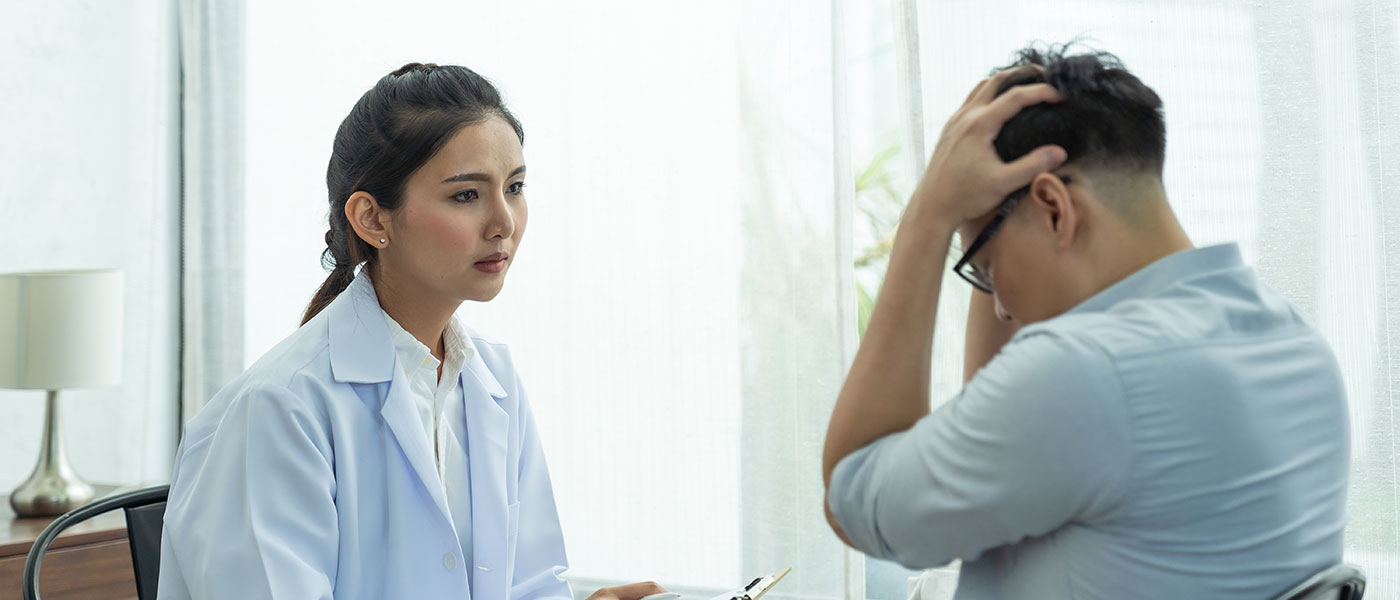
Salvia divinorum is a psychoactive plant that produces intense, short-acting hallucinogenic effects through its active compound salvinorin A [1]. Effects typically begin within seconds and last 15 to 30 minutes, though they may feel much longer due to severe time distortion. Salvia causes overwhelming hallucinations, dissociation, loss of coordination, and unpredictable psychological reactions. While fatal overdose is rare, salvia is dangerous due to the risk and potential for triggering lasting psychological harm.
What Is Salvia Divinorum?
Botanical and Historical Background
Salvia divinorum, also called diviner’s sage, Sally-D, or magic mint, is a psychoactive plant in the mint family native to Oaxaca, Mexico. Indigenous Mazatec people have historically used salvia in spiritual and healing ceremonies [2]. The plant contains salvinorin A, one of the most potent naturally occurring hallucinogens known [3].
In recent decades, salvia has become known outside traditional contexts, particularly among young people seeking novel psychoactive experiences. However, ceremonial use within a structured cultural framework differs significantly from recreational use, which often lacks the safeguards of traditional practices.
How It’s Used
People use salvia in several ways. Smoking dried leaves or concentrated extracts is most common, producing effects within seconds. Chewing fresh leaves produces a slower onset and longer duration. Brewing salvia as tea is less common and produces milder effects.
A critical safety concern is the wide variability in extract potency [1]. Concentrated extracts can be many times stronger than natural leaves, making it difficult to predict intensity and increasing the risk of overwhelming experiences.
How Salvia Affects the Brain and Body

Active Compound and Mechanism
The active ingredient in Salvia, Salvinorin A, acts primarily on kappa-opioid receptors in the brain, unlike classic psychedelics like LSD or psilocybin, which target serotonin pathways [3]. This unique action produces distinctly different experiences, often described as more intense, disorienting, and unpredictable.
Immediate Perceptual and Cognitive Effects
The most prominent Salvia divinorum effects involve dramatic alterations in perception and consciousness [1]. Visual and auditory hallucinations can be extremely vivid and bizarre, with people reporting geometric patterns, distorted environments, or entirely alternate realities.
An altered sense of time and reality is characteristic. Time may seem to stop, speed up dramatically, or become meaningless. Many users describe feeling trapped in experiences that last subjectively for hours but objectively last only minutes.
Dissociation and out-of-body sensations are common. People may feel completely separated from their physical body, believe they’ve become objects or other people, or feel merged with their surroundings. Distorted body perception and loss of coordination frequently occur, with severe loss of motor coordination making walking or maintaining balance nearly impossible [4].
Physical Sensations
Physical effects include sensations of heaviness or floating, profound dizziness, and altered balance. Some people experience changes in heart rate, sweating, or nausea. Many users become unable to stand, walk, or perform basic tasks safely during intoxication.
Emotional and Psychological Reactions
Emotional responses are highly unpredictable. Some people experience brief euphoria or uncontrollable laughter, while many experiences involve intense fear, panic, paranoia, or a sense of impending doom. Confusion and inability to recognize familiar people or places are common. The psychological intensity often exceeds what users anticipate, even those experienced with other psychedelics.
Is Salvia Dangerous? Evaluating the Risks
While salvia rarely causes fatal overdose, it carries significant risks that make it potentially dangerous.
Short-Term Acute Risks
| Risk Category | Specific Dangers | Why It Happens | Prevention Considerations |
| Accidents and Injuries | Falls, burns, collisions, wandering into traffic | Severe loss of coordination and awareness | Never use alone; requires a sober sitter |
| Acute Panic | Overwhelming fear, terror, feeling of dying | Intense dissociation and loss of reality | Pre-existing anxiety increases risk |
| Dangerous Behavior | Self-harm, aggression, escape attempts | Complete disconnection from reality | May require physical restraint |
| Choking Risk | Risk of vomiting while impaired | Nausea combined with loss of awareness | Never leave a person alone |
The most immediate danger comes from accidents during intoxication. Because salvia produces profound disorientation and loss of coordination, people may fall, walk into dangerous situations, or injure themselves without awareness.
Acute panic attacks and overwhelming psychological distress are common. The intensity can produce genuine terror, with users believing they’re dying, trapped forever, or have permanently lost their sanity.
Psychological Dangers
Salvia can trigger or worsen underlying mental health conditions. People with a predisposition to anxiety disorders, depression, or psychotic disorders face a heightened risk. Some individuals experience persistent anxiety or depressive symptoms after the use of Salvia that continue long after the immediate effects wear off.
The unpredictability means even experienced users cannot reliably predict whether an experience will be manageable or traumatic. Many users describe their salvia experiences as among the most frightening of their lives.
Understanding Risk for People in Recovery
If you’re in recovery from substance use or managing mental health conditions, salvia poses particular risks. The intense dissociation can be destabilizing for people working to maintain emotional balance and sobriety. Salvia use can trigger cravings for other substances, disrupt recovery progress, or exacerbate underlying conditions like anxiety, depression, or trauma-related symptoms.
Duration and Onset of Effects
When smoked, salvia effects typically begin within 30 seconds to 2 minutes, peak rapidly, and decline within 15 to 30 minutes. However, the subjective experience of time is so distorted that experiences lasting minutes can feel like hours or days.
When leaves are chewed or brewed as tea, the onset is slower (10 to 20 minutes), and the duration is longer (up to an hour or more), but the effects are generally less intense.
While acute hallucinogenic effects wear off relatively quickly, psychological aftereffects can persist. Many people feel disoriented, confused, emotionally shaken, or mentally exhausted for hours afterward. Some report lingering anxiety, mood changes, or difficulty concentrating for days or longer.
Potential Long-Term Effects and Concerns
Limited Research Landscape
Scientific research on the long-term effects of salvia remains limited. Most available information comes from anecdotal reports and case studies rather than large-scale controlled studies, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about long-term risks.
Reported Long-Term Psychological Symptoms
Some individuals report persistent psychological symptoms following salvia use, including ongoing anxiety, depression, or mood instability. Memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and cognitive disturbances have been documented in some users.
Some people describe lasting changes in perception or consciousness, including brief flashbacks or persistent feelings of unreality. For individuals predisposed to psychiatric conditions, salvia may trigger or unmask conditions that persist long-term.
Dependence and Functional Impact
Salvia is not commonly associated with physical dependence. However, some individuals develop patterns of repeated use or psychological preoccupation with the experience that can resemble substance use disorder. Some regular users report social withdrawal, reduced motivation, or difficulty maintaining goal-directed behavior.
Safety and When to Get Help
Seek immediate help if someone using salvia shows prolonged distress lasting beyond the expected duration, engages in dangerous behavior, cannot be calmed after the effects have worn off, shows signs of injury, or appears to be having a medical emergency.
Contact mental health professionals if someone experiences intense or lingering anxiety lasting days or weeks after use, symptoms of psychosis, thoughts of self-harm, or inability to function in daily life.
At Discovery Institute in Marlboro, New Jersey, we understand that experimentation with substances like salvia often reflects deeper struggles. If you or someone you love is using salvia or other substances and experiencing concerning effects, compassionate help is available. Our team provides medical detox, residential addiction treatment, intensive outpatient services, therapy programs addressing both substance use and co-occurring mental health conditions, and family support programs. You don’t have to navigate these challenges alone.
Legal and Context Considerations
Salvia’s legal status varies significantly by location. In the United States, salvia is not federally controlled but is banned or restricted in many individual states. Many countries have banned salvia entirely. It’s crucial to understand that legal availability does not mean a substance is safe.
Informed Awareness Matters
Salvia divinorum produces intense, short-lived changes in perception and consciousness through its unique action on kappa-opioid receptors. While fatal overdose is rare, the unpredictable and often overwhelming effects create real risks for accidents, injuries, and psychological harm [4].
Understanding what happens if you smoke salvia includes recognizing both the immediate hallucinogenic effects and the potential for lasting psychological impact [5]. The intensity and unpredictability of experiences, combined with significant loss of physical coordination during intoxication, create a risk profile that deserves serious consideration.
If you’re struggling with substance use, mental health challenges, or the aftermath of difficult experiences with salvia or other substances, help is available. You deserve support and the opportunity to build a healthier relationship with yourself and your well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Salvia produces intense hallucinogenic effects, including vivid hallucinations, severe time distortion, dissociation from your body and surroundings, loss of coordination, and unpredictable emotional reactions ranging from euphoria to terror [1]. Effects begin within seconds when smoked and typically last 15 to 30 minutes.
Smoking salvia produces the most intense and rapid-onset effects. Within 30 seconds to 2 minutes, you’ll experience powerful hallucinations, complete loss of coordination, severe dissociation, and altered perception of time and reality. You likely will be unable to walk or perform basic tasks safely during the experience.
Yes, salvia carries significant hallucinogen risks despite rarely causing fatal overdose [4]. Primary dangers include accidents and injuries during intoxication due to severe loss of coordination, acute panic attacks and overwhelming psychological distress, triggering or worsening underlying mental health conditions, and unpredictable experiences that can be genuinely traumatic.
While research is limited, some users report long-term psychological effects, including persistent anxiety, depression, memory problems, and difficulty concentrating [5]. Salvia may trigger or unmask latent psychiatric conditions in vulnerable individuals. Some people experience flashbacks or persistent feelings of unreality after use.
When smoked, acute effects typically last 15 to 30 minutes, with onset within 30 seconds to 2 minutes. Time distortion during the experience makes it feel much longer. Chewing leaves or drinking tea produces a slower onset (10 to 20 minutes) and longer duration (up to an hour). Psychological aftereffects can persist for hours or days.
Historically, Mazatec people in Mexico used Salvia divinorum in spiritual and healing ceremonies. In modern contexts, people primarily use salvia recreationally, seeking novel hallucinogenic experiences. Some researchers study salvia’s unique mechanism, but it is not approved for any medical use.
Salvia’s legal status varies by location. In the United States, salvia is not on the list of federally controlled substances but is banned or restricted in many individual states. Many countries have banned salvia entirely. Legal status is not an indicator of safety, and legality varies and changes over time.
Find out how we can help
Our compassionate counselors are standing by to answer any questions you may have. After helping thousands of people over the last 50 years, we have the resources to help you and your family and all your individual needs.
[1] National Institute on Drug Abuse. (n.d.). Hallucinogens and dissociative drugs (Research Report Series) [PDF]. https://nida.nih.gov/sites/default/files/hallucinogensrrs.pdf
[2] Siebert, D. J. (1994). Salvia divinorum and salvinorin A: New pharmacologic findings. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 43(1), 53–56. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7526076/
[3] Roth, B. L., Baner, K., Westkaemper, R., Siebert, D., Rice, K. C., Steinberg, S., Ernsberger, P., & Rothman, R. B. (2002). Salvinorin A: A potent naturally occurring nonnitrogenous κ opioid selective agonist. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 99(18), 11934–11939. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC129372/
[4] Johnson, M. W., MacLean, K. A., Reissig, C. J., Prisinzano, T. E., & Griffiths, R. R. (2011). Human psychopharmacology and dose-effects of salvinorin A, a kappa opioid agonist hallucinogen present in the plant Salvia divinorum. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 115(1–2), 150–155. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21131142/
[5] Johnson, M. W., MacLean, K. A., & Griffiths, R. R. (2012). Dose-related effects of salvinorin A in humans: Dissociative, hallucinogenic, and memory effects. Psychopharmacology, 220(3), 567–580. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23135605/